GMP certificate is one of the highest standards for manufacturing and quality control in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries. To answer some questions about the GMP standard: What is GMP? What does a GMP-certified factory need? What is the role of this standard in the production of functional foods? We’ll answer all these questions below.
Learn more: The leading & trusted wet tissue manufacturer in the market
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing practice and is a set of regulations established by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to ensure consistent quality in the production of goods, including supplements and pharmaceuticals.

A product bearing the GMP seal/certification indicates that it was made in a facility approved by the FDA
Read more: What is the ISO 9001:2015 standard? Benefits & 7 Principles [updated]
Good manufacturing practices certificate (GMP) covers every aspect of production, from materials and location to staff training and equipment. Written procedures are a critical part of any process that could affect the finished product’s quality. Each step of the manufacturing process must come with documented proof of methods used to ensure consistency across all products.
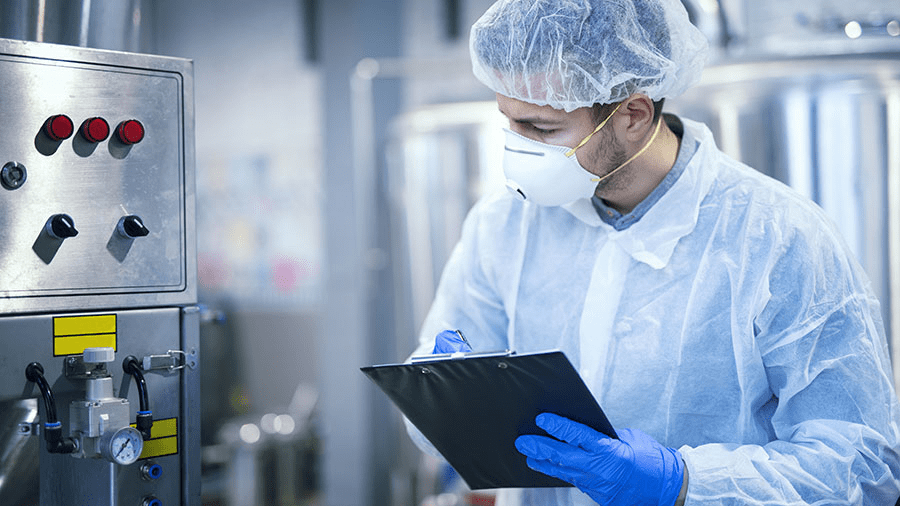

Written procedures are required in the whole GMP processing
These standards are applicable to the production of:
Pharmaceutical, beverages, cosmetics,… manufactures should own GMP certificate
The GMP regulations address a variety of issues, including record keeping, personnel qualifications, sanitation, cleanliness, equipment verification, process validation, and complaint handling. These are general and open-ended requirements that give manufacturers flexibility in implementing controls that make sense for their businesses.
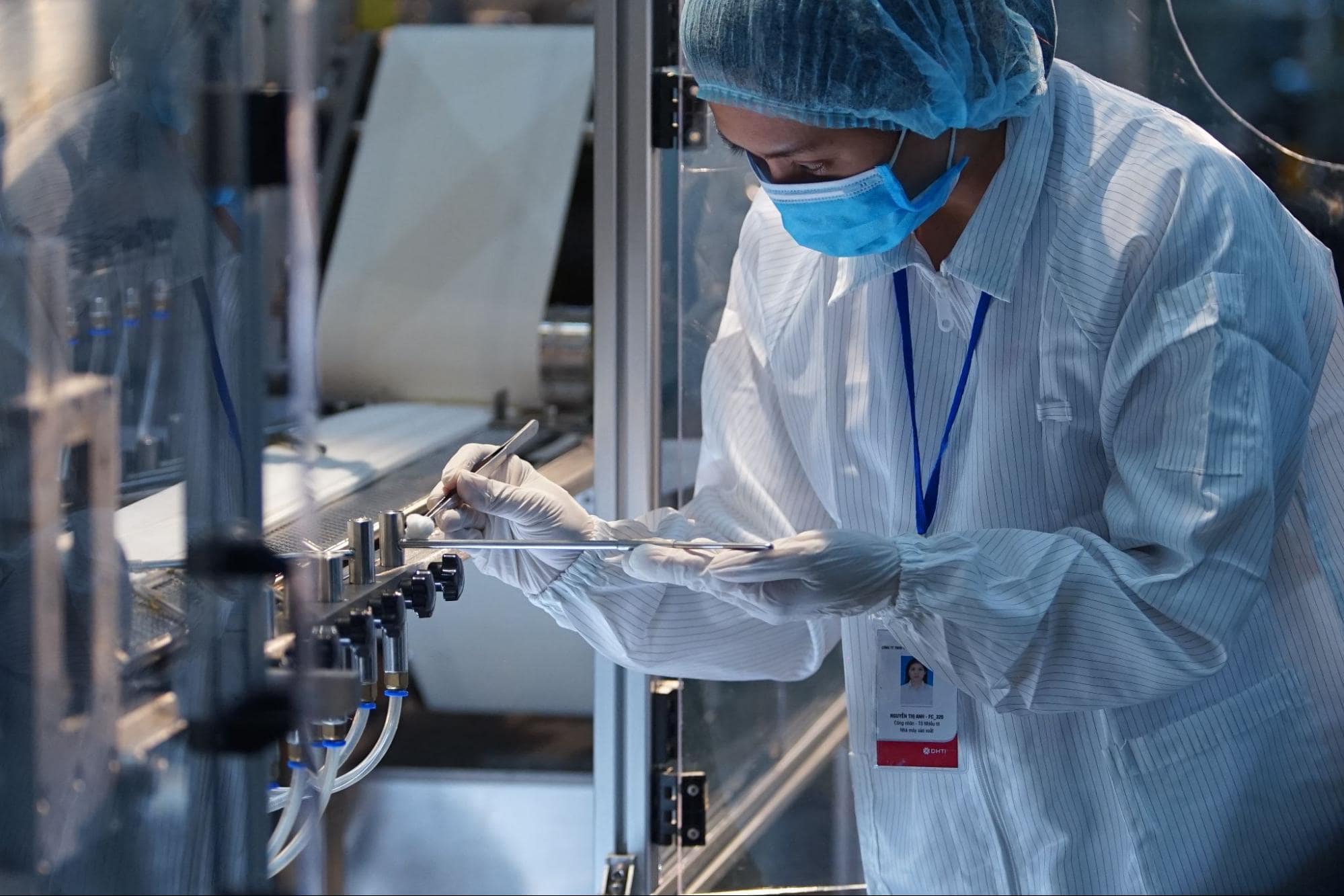

Sanitation, cleanliness, equipment verification are parts of GMP requirements
GMP is often referred to as cGMP, which stands for current Good Manufacturing Practices. The “c” reminds manufacturers that they must employ up-to-date systems and technologies in order to comply with regulations. Some of the systems and equipment used to prevent contamination, mixups, or errors in a processing plant may have been first-rate 20 years ago but are less than adequate by today’s standards.

Manufacturers need to update their equipment and facilities in order to comply with GMP qualifications
Here are some benefits for a good manufacturing practices certificate:
1.2.1 For The Manufacturer
Businesses and organizations that apply GMP certification requirements to the production process can gain significant benefits, including:
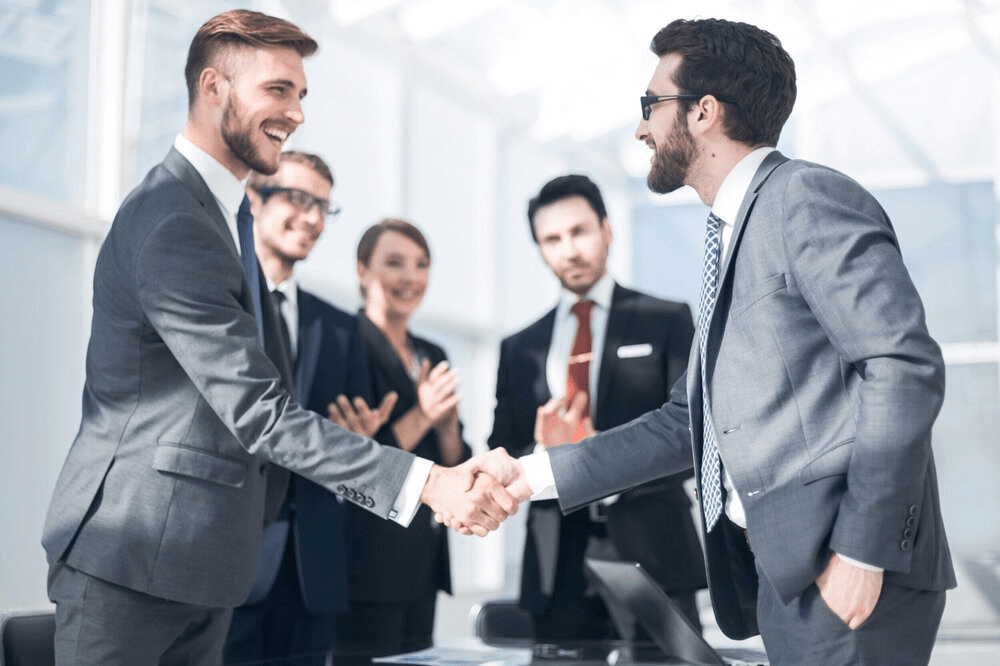

GMP certification helps companies build long-lasting relationships with customers and business partners
1.2.2 For The Customer
Consumers will benefit from GMP standards because they are made to feel safe, assured that the products/services they choose meet high quality standards, and know their health is not in danger.
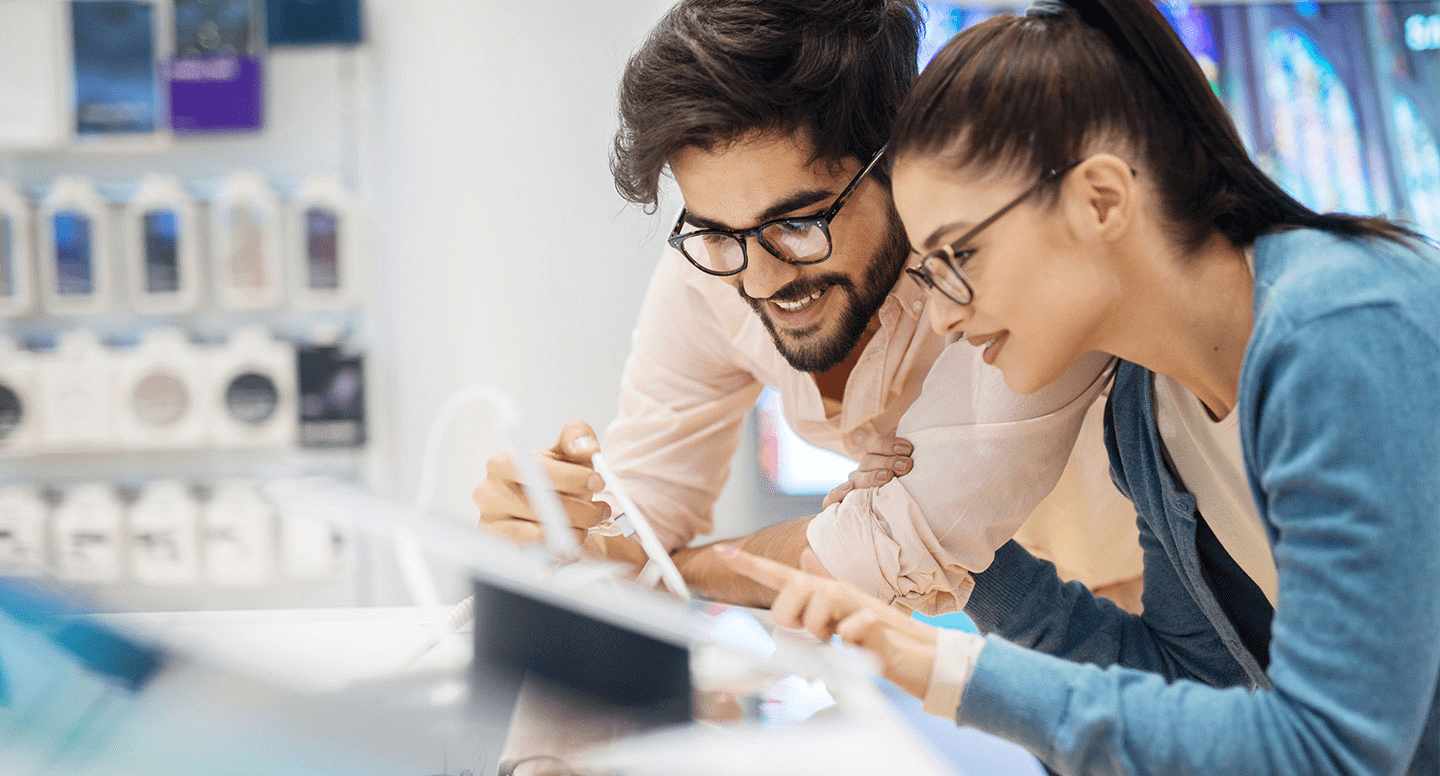

Customers feel more comfortable buying products that carry a GMP certificate
This is the answer for question “Is GMP certificate important to manufacturing?” – Good manufacturing practices (GMP) certificates are crucial, not only for earning customers’ trust but also building long-term loyalty and increasing profits.
Here are five components (Product – People – Processes – Procedures – Premises) that manufacturers need to know to obtain good manufacturing practices certificate quickly:
1 – Products
Primary materials are the raw ingredients used to produce a finished product, which is sold to consumers. If primary materials are of low quality, flaws can occur in the end result. Therefore, one of the core GMP certification requirements is that all products must have a master formula that is followed exactly throughout manufacturing. A quality assurance system composed of regular testing and comparisons ensures this.

GMP qualifications require that manufacturers follow a standardized formula for making products
2 – People
All employees are expected to be familiar with and adhere to strict manufacturing processes and regulations. A current GMP training must be undertaken by all staff members so that they understand their roles and responsibilities in regard to these policies. Staff assessment helps boost productivity, efficiency, competency—and ultimately the bottom line of your company’s financial statements.

All staff members must undertake a current GMP training so that they understand their roles and responsibilities in regard to the policies
3 – Processes
Processes should be documented, clear, consistent, and accessible to all employees. Regular evaluation should be conducted to ensure that all employees are complying with current processes and meeting the organization’s standards.
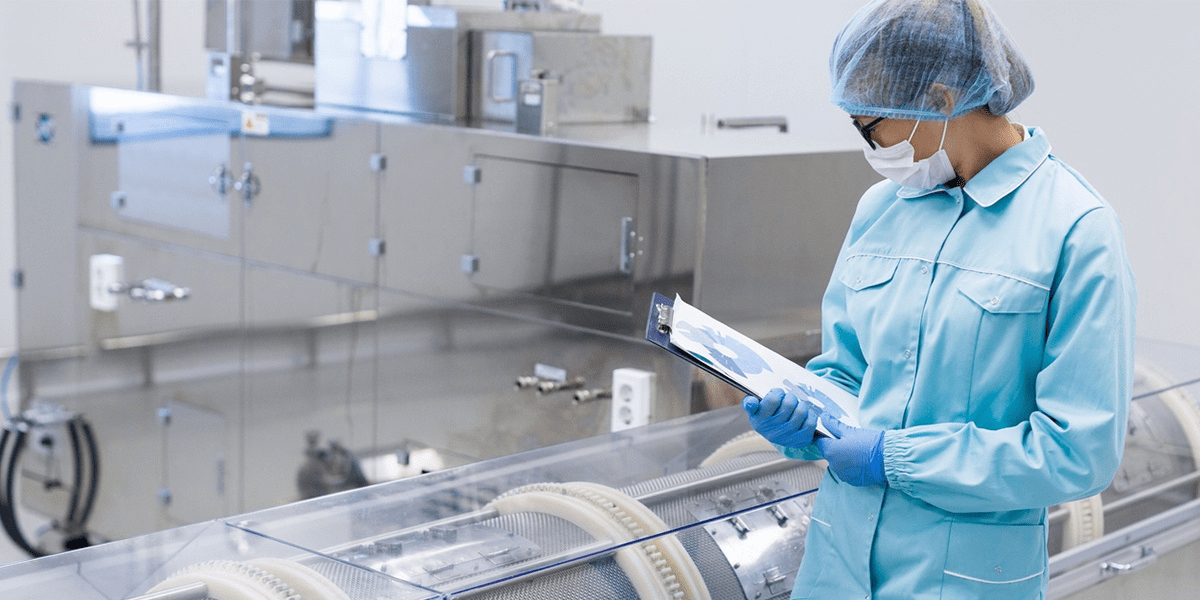

Company should have clearly defined processes, and employees should be trained to follow those processes
4 – Procedures
Procedures are sets of guidelines put in place to ensure that a process or part of it is carried out consistently. All employees should be made aware of these procedures and instructed on how they work. Any deviation from standard procedure should be reported and investigated immediately.
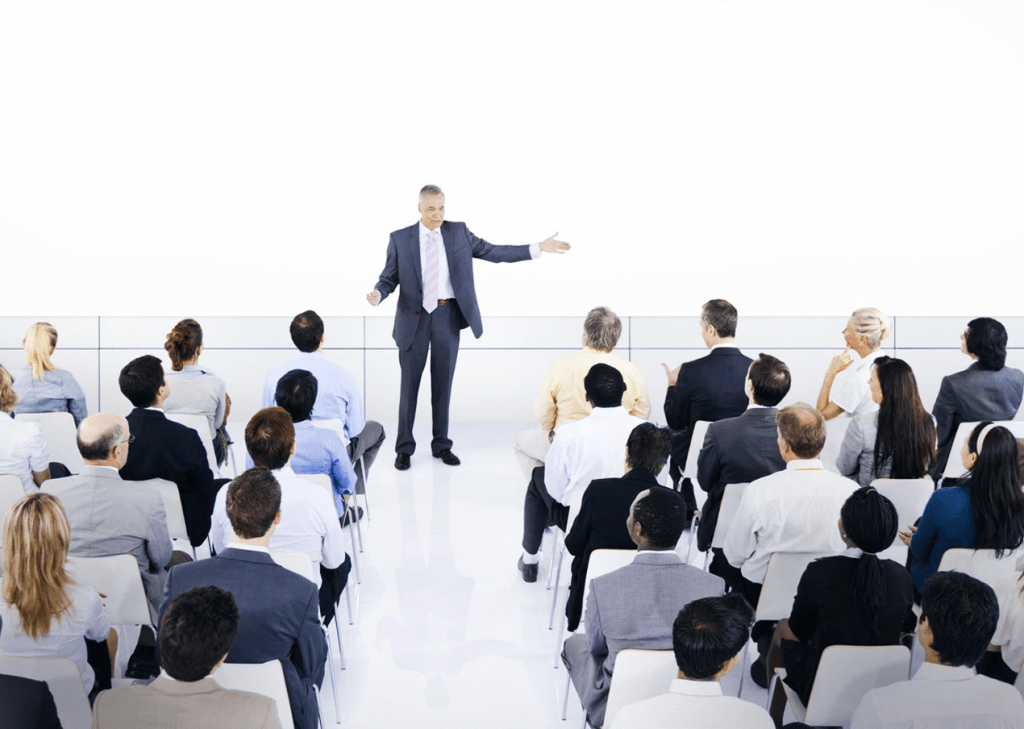

All employees should have access to detailed, lucid, consistent, and transparent procedures
5 – Premises
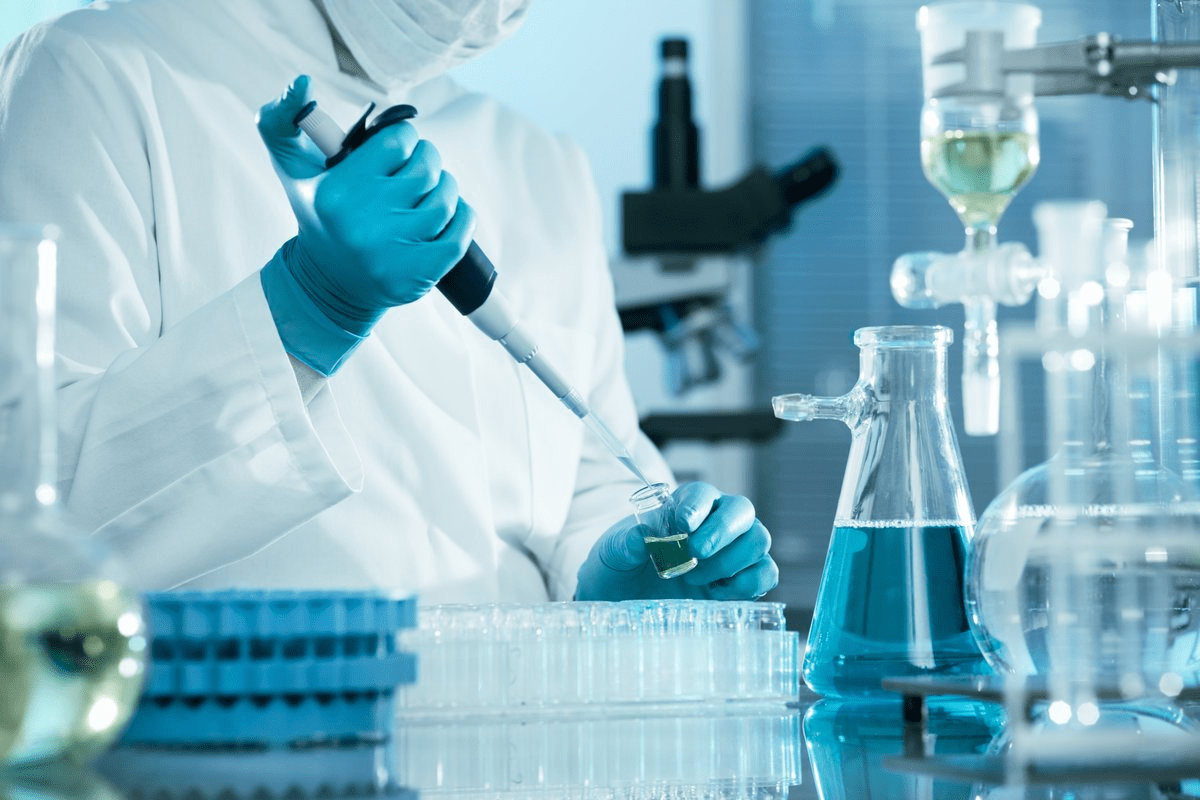
Facilities, laboratories, and equipment must be maintained in a safe, sanitary, and effective manner. These include proper cleaning and storage along with other measures that can be taken to achieve consistent results, lower the risk of equipment failure, and ensure timely repairs. The goal is to reduce product variations and protect customers, and team members from operational issues onsite.
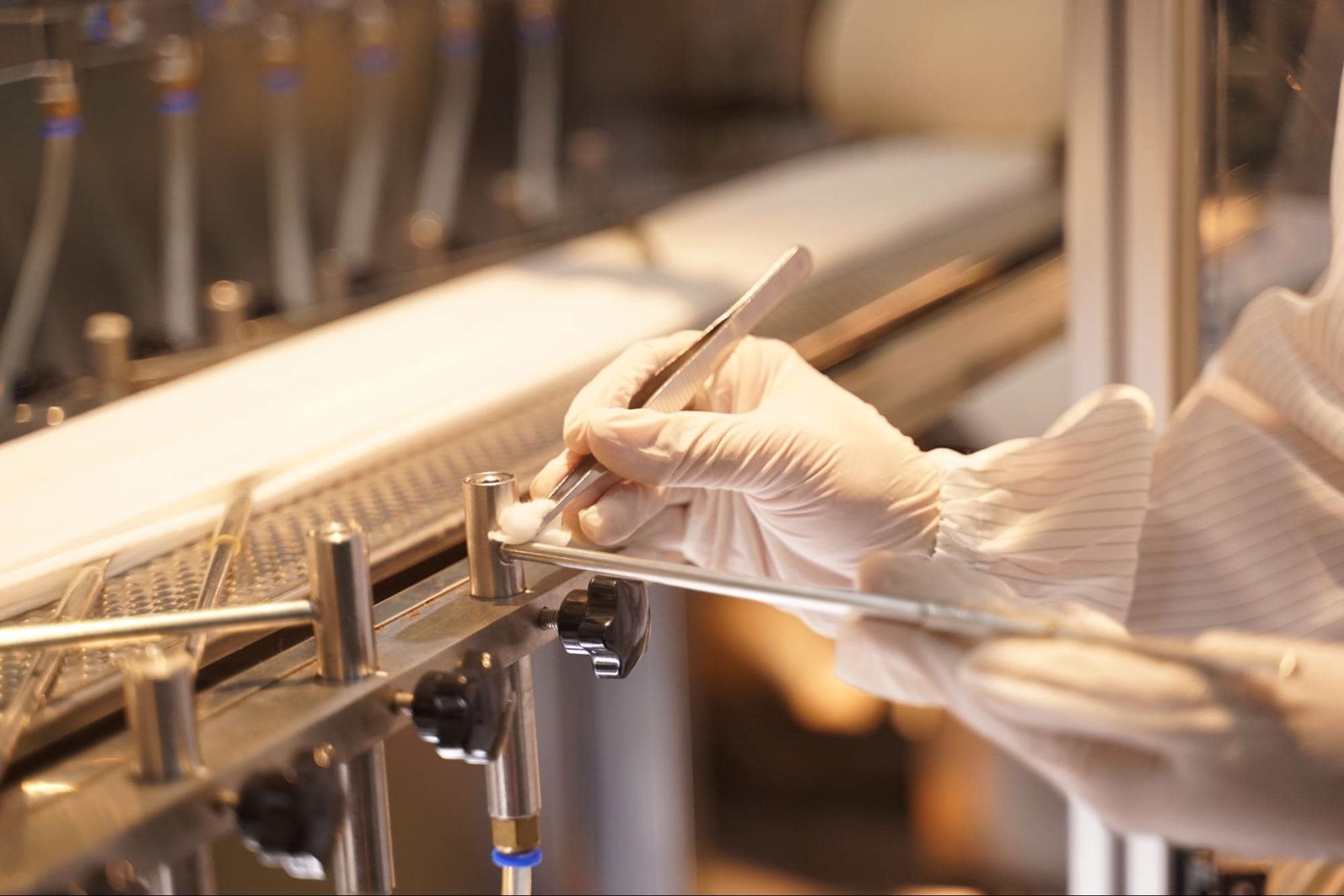

To meet GMP qualification requirements, manufacturers must regularly clean and maintain facilities, laboratories and equipment
Application
The initial step to obtaining a GMP certification is submitting an application that covers essential information about the company and its operations.The affirmation body must acknowledge the application, record all data and ensure that database is kept up-to-date.
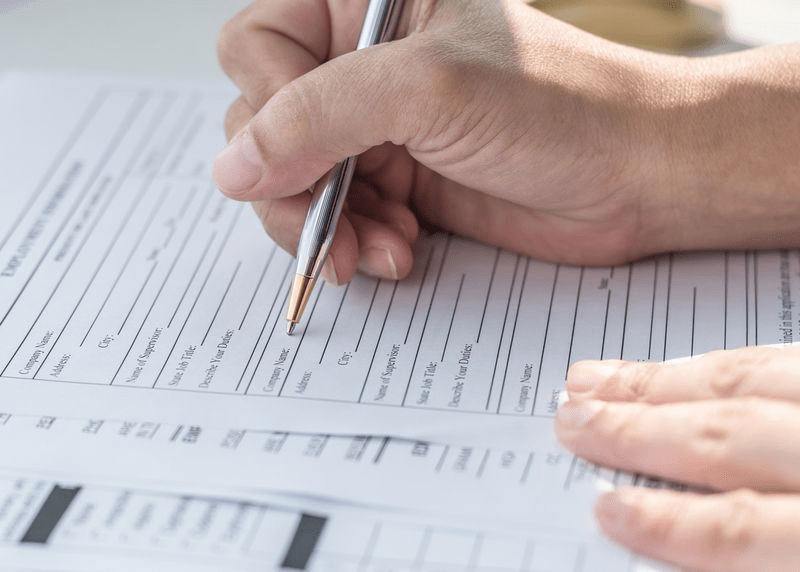

Firms need to provide all general information in the GMP application form
Review Of Application
The application will be evaluated by the group to ensure that it meets consistency requirements.

Check that application information is consistent and complete
Analysis & Agreement
After the audit of documents, a gap analysis is performed to make sure that all areas are covered by quality guidelines. The gap analysis compares what is supposed to be done with what has been accomplished.
Documentation Review
Check the organization’s documentation to confirm that it meets compliance standards.
Stage-1
Analyze your associations’ recorded approaches and strategies for consistency.
Then, review the documentation of your administration structure to ensure that consistency requirements have been met.
When a noncompliance occurs, corrective action must be taken.
Verify the documentation of an establishment to conform to standard requirements.
Stage-2
The inspector checks that the association is in compliance with its documentation, and an examiner of an authoritative body verifies the noncompliance. Afterward, the reviewer offers a chance to address the noncompliance. Then review the execution procedure as per the association’s report.
If there is any non-similarity between the actual and planned results, then remedial action has to be taken.
Ensure that your representatives are following the work guidance and then executing on those instructions.
Granting Of Certification
The Certification Body will grant a certificate of compliance that is valid for many years.
Surveillance Audit
Surveillance review is required in order to guarantee that the association meets the prerequisites of its administration framework. Observational monitoring must be carried out every six months or one year, depending on when it was first issued with a certificate.
A GMP certificate is valid for three years from the date of the most recent inspection; however, the period of validity can be shortened if circumstances warrant. A good manufacturing practices certificate refers to a specific inspection and cannot be renewed until a new inspection is conducted.
The cost of getting a Good Manufacturing Practice certificate is determined by the size of a business.

The cost of a good manufacturing practices certificate varies depending on the size of your business and other details
The following table shows the average cost per establishment by size:
| Number of
Employees |
Annual Revenue | Setup Costs* | Annual Costs* | |
| Small
Establishments |
<20 | Under $1 Million | $26,000 | $46,000 |
| Medium
Establishments |
20 – 500 | $5 to $10 Million | $20,000 | $184,000 |
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has calculated that:

For a large company, the cost of GMP compliance can run up to $204,000 each year
When you work in any manufacturing industry, compliance with good manufacturing practices is vital for your business. Not only does it help you make a high-quality product, but it also upholds consumer and ecological health. . However, if manufacturers do not comply with GMP guidelines, there will be consequences; let’s take a look at some of them:
1 – Strike To Reputation & Goodwill
For all businesses, reputation is crucial. Without satisfied customers, you can’t build a successful business. With poor manufacturing practices, your reputation will suffer. Customers won’t trust a company they believe produces shoddy products.
2- Failure Of Consumer Confidence
Good manufacturing practices are in place to keep your clients safe. If you do not adhere to these guidelines, consumers will lose confidence in your product. But the penalties for not following the guidelines are greater than just a business break for your company; they could result in legal action or even jail time if severe enough violations are occurring.

Not following GMP regulations may result in a loss of customer confidence
3 – Criminal Prosecution
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has the authority to stop production of a drug through a court injunction. If circumstances warrant it, the Department of Justice (DOJ) and Health and Human Services (HHS) also have the authority to take legal action against any company that violates good manufacturing practices.

The DOJ and HHS may prosecute a company that violates good manufacturing practices
4 – License Cancellations
When manufacturing a product, several licenses are required. These include building permits, licensed physicians at the facility, and facility licenses. Failure to comply with good manufacturing practices guidelines puts a company at risk of losing these licenses.

Failure to adhere to GMP guidelines can lead to the cancellation of your certificate
5 – Indictment Of Fraud
Failure to comply with good manufacturing practices can lead to fraud charges. Mislabeling ingredients or failing to advertise a product in compliance with good manufacturing practices guidelines are examples of fraudulent acts. When a company accused of fraudulent behavior is in the manufacturing sector, the consequences can be severe.
If a company mislabels ingredients or fails to disclose information about their product, they can face legal action
The GMP regulations prohibit fraudulent labeling and branding practices. Violations of these regulations can lead to serious consequences for manufacturers.
Helpful information about wet wipes production:
GMP certificate is a prestigious qualification for manufacturers. We hope that the information above has been helpful in obtaining this certification, and we also recommend following our other related articles to stay up-to-date with important news in your field of manufacturing.
Dong Hiep Trading and Investment Joint Stock Company